Did you know Google and Yahoo! are setting new rules for sending emails? Do you have an idea of how this could impact your business as an email marketer, business owner, or blogger?
Just in case you’ve not heard about it, back in October of 2023, both Google and Yahoo! announced that they would be implementing new email sender requirements this coming February. You read that right, this February, 2024.
Now, what caught my attention is that both Google and Yahoo! announced these new rules on the same date (3rd October 2023) and gave the same month (February 2024) as the end date. This, for me, was enough to take the announcement with all seriousness!
And, so I took some time to carefully go over these rules to understand what they are and how they will impact email deliverability, in the coming months and years. I dare say, this is going to be huge! Non-compliant will definitely impact significantly on email deliverability as your emails could be marked as spam or even blocked entirely.
But not to worry, in this post, I’m here to help you navigate these changes so you can do the needful and ensure your emails continue to reach their intended recipients. We’ll help you understand each of the requirements, explain their purpose, and discuss their impact on email deliverability.
I’ll also provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to implement the changes, offer insights on optimizing your email performance, and even share some advanced techniques. By the end of this post, you’ll have a clear understanding of the new requirements and be well-equipped to maintain, if not improve your email deliverability.
You want all of these right? Then let’s dive right in!
What Are The New Email Sender Requirements?

The new email sender requirements from Google and Yahoo are a set of rules designed to combat spam and improve email security. This set of rules is not new. They have been considered best practices for email authentication over the years. However, starting in February 2024 Google and Yahoo! are turning them into mandatory requirements.
These requirements primarily target large bulk senders, particularly those who send more than 5,000 emails a day. The key points of this new senders rules include:
- Email Authentication: Senders are required to authenticate their emails using DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), SPF (Sender Policy Framework), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance).
- Spam Complaint Rate: Senders must maintain a spam complaint rate under 0.3%.
- Unsubscribe Process: Senders must allow people to unsubscribe by clicking just one link, and honor unsubscribes within two days.
- Compliance with RFC 5322, PTR records, and rDNS: Senders must ensure their sending server IP addresses have valid reverse DNS records.
- TLS Connection: Senders must use a TLS connection for transmitting email.
These changes aim to deliver fewer unwanted messages and better inbox experiences to email users. Non-compliance with these requirements can lead to emails being marked as spam or even blocked entirely. Therefore, email senders must understand and prepare for them.
Related: How to Harness the Simple Power of Email Marketing to Profit Online
The New Email Sender Requirements Explained
Let’s now dive into each requirement so we can truly understand what it means and its impact on email deliverability.
1. SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
SPF is an email authentication method designed to prevent spammers from sending emails on behalf of your domain. By creating an SPF record in your Domain Name System (DNS), you can specify which mail servers are authorized to send emails from your domain.
When an email is sent, the receiving server checks whether the associated domain has an SPF record and acts accordingly. If the sender’s IP address isn’t listed in the SPF record, the email fails SPF authentication and is either rejected or sent to the spam folder.
The impact of SPF on email deliverability is significant. Without an SPF record, your emails are more likely to be marked as spam or rejected by email providers.
2. DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
DKIM provides an encryption key and digital signature that verifies that an email message was not faked or altered. This is done by adding a digital signature linked to your domain name in the email headers. The recipient’s email server then uses the sender’s public key to check if the email was indeed sent by the owner of the domain and hasn’t been tampered with during transit.
Like SPF, DKIM is essential for email deliverability. Emails without a valid DKIM signature may be treated as spam.
3. DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance)
DMARC works with SPF and DKIM to authenticate mail senders. DMARC ensures the destination email systems trust messages sent from your domain. Using DMARC with SPF and DKIM gives organizations more protection against spoofing and phishing emails and improves the deliverability of your emails.
DMARC helps receiving mail systems decide what to do with messages from your domain that fail SPF or DKIM checks.
Before implementing DMARC, you must first deploy SPF and DKIM, the two primary authentication protocols. The DMARC email authentication protocol was designed to complement and enhance SPF and DKIM, reinforcing their strengths while also addressing their shortcomings.
4. Bulk and Non-Bulk Sender Requirements
The requirements for bulk and non-bulk senders differ slightly. Bulk senders, such as email marketers and businesses, need to pay particular attention to their spam complaint rates, as high rates can lead to email delivery issues.
5. The 0.3% Spam Rate Threshold
Google and Yahoo have set a spam rate threshold of 0.3%. If your emails exceed this rate, you may experience deliverability issues.
Strategies for keeping your spam rate low include maintaining a clean and engaged email list, regularly checking your email content for spam triggers, and ensuring a smooth unsubscribe process for your recipients.
Why Every Email Sender Should Care About the New Rules
So, why should you care about these new Google and Yahoos new requirements? Yes, they may have indicated these requirements for bulk senders, but as an email marketer you should care for the following reasons:
- Enhanced Security Measures: Google and Yahoo are implementing advanced security protocols to ensure that emails are secure, user-friendly, and devoid of spam.
- Trust and Identification: The updated guidelines necessitate that bulk senders authenticate their emails, simplifying the process for recipients to identify and trust the email source.
- Impact on Deliverability: Failing to adhere to the new guidelines can have a substantial effect on email deliverability to Gmail and Yahoo accounts.
- Spam Prevention: The guidelines emphasize authentication, controlling spam rates, and streamlining unsubscription procedures to mitigate spam and bolster inbox security.
- Industry Collaboration: The modifications are a result of joint initiatives from Google and Yahoo, to implement new protective measures for recipients.
- Sender Reputation and Compliance: Compliance with the new guidelines is vital for preserving the sender's reputation, ensuring optimal deliverability, and fostering trust with the audience.
- Global Impact: Given Gmail’s global market share of 29.67%, the new guidelines aim to shield nearly 2 billion users from spam or undesired messages.
- Preparation for Future Changes: The updated rules for email authentication are expected to become a standard for all senders in the future, underscoring the importance for all email senders to stay informed and ready.
- Provider-Specific Differences: While Google’s guidelines are more stringent, aligning with Google’s rules will also ensure compliance with Yahoo’s rules, highlighting the need to comprehend the subtleties of each provider’s regulations.
- Universal Compliance: Even though some guidelines currently target high-volume senders, all senders must recognize and prepare for these changes, as they may become relevant to all senders in the future.
For the above reasons I believe that the new email sender guidelines set by Google and Yahoo are of great significance to all email senders, as they seek to strengthen security, combat spam, and enhance the overall email experience for users. Non-compliance can result in deliverability problems, making it crucial for senders to understand, prepare for, and adhere to these new guidelines.
Implementing the New Sender Rules
Now that we have an understanding of what these new email sender requirements are and how they could impact your marketing efforts, let’s now explore how you can implement them. But first, there are a few prerequisites you need to have in place. You should have ownership of the domain you’re sending emails from and a basic understanding of DNS records.
It will interest you to know that with the new rules, it’s expected that you own the domain name, or at least, have access to the domain you’re sending emails from. Starting in February, you’ll not be able to use Yahoo! or Google email addresses as your “From” emails.
I recommend that you get your domain names from NameCheap.com. They remain the best in the industry as far as I know.
DNS (Domain Name System) records are instructions that live in authoritative DNS servers and provide important information about a domain, including what IP address is associated with that domain and how to handle requests for that domain. Specifically, it is essential to set up and maintain valid reverse DNS records, also known as PTR records, for your sending domain and IP address. This connection is crucial for establishing trust and credibility in the eyes of email providers.
The specific types of DNS records that come into play when it comes to these new email sender requirements, are SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. These are what is used to authenticate your emails.
That being said, here’s how to set up your domain and implement the different DNS records to meet the new email sender requirements.
(Please note that the exact steps to set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC can vary depending on your email service provider. You may need to refer to your provider’s specific documentation or support services for detailed instructions.)
Step 1: Verify Your Domain
You need to verify your domain with your email service provider. This process typically involves adding a TXT record to your domain’s DNS settings. This is what authenticates that you own or have administrative access to the domain you’re sending emails from. Different web hosts provide different ways on how to do this.
In this guide, I’m using Hostinger as an example. Over the past 10+ years I have used different hosting services however, I think, Hostinger makes this process a lot simpler than most of the hosting services I have used. Here’s how to do with Hostinger:
- Login to your hpanel dashboard and under “Websites” select the domain you want to add the DNS record.
- Click on the “Advanced” tab, and then “DNS Zone Editor.” This will open the DNS Zone Editor. From here you can easily add the different DNS records to verify your domain
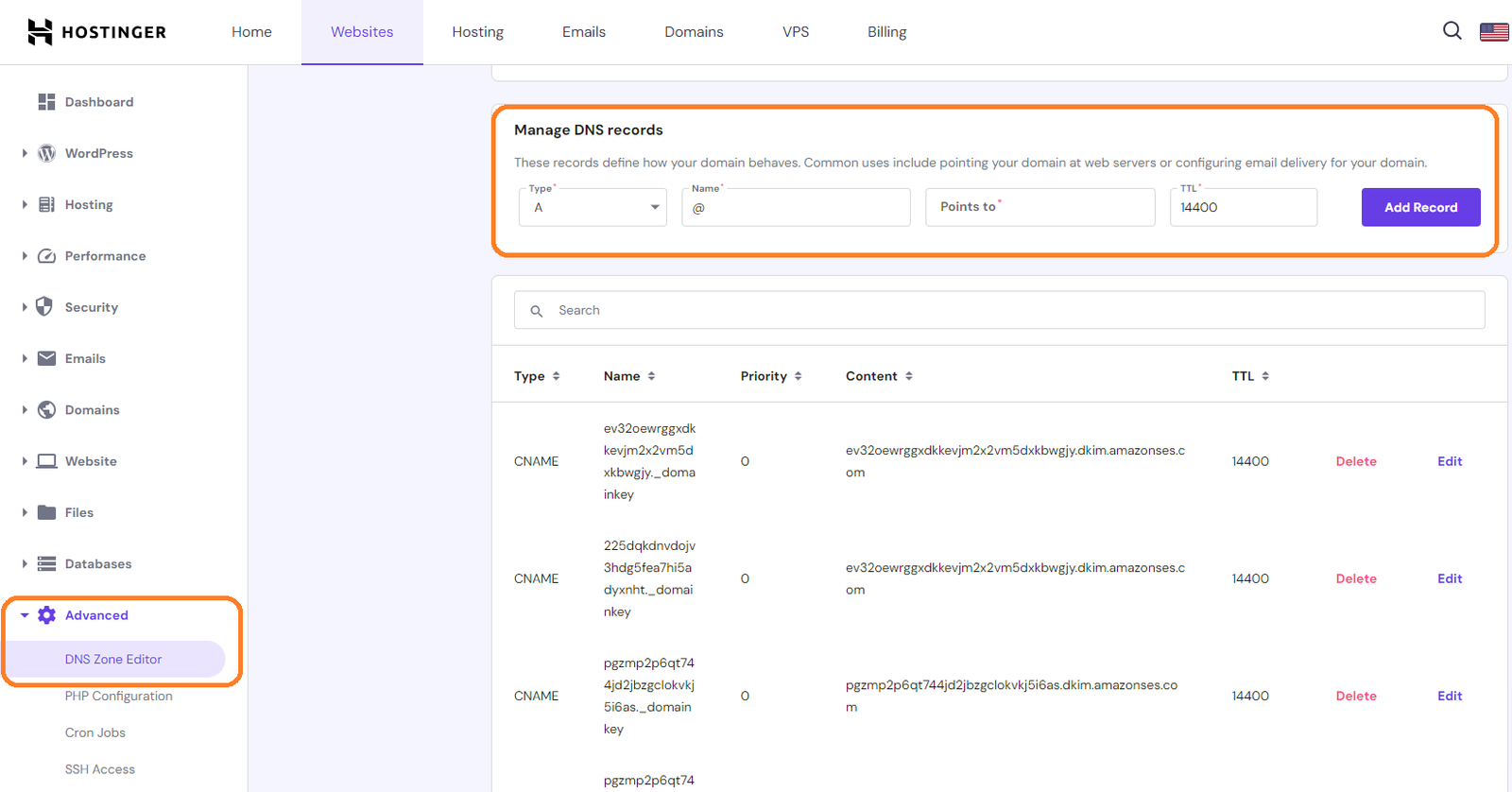
Step 2: Implement SPF
As we have mentioned earlier, SPF (Sender Policy Framework) records specify which servers are allowed to send emails on behalf of your domain. Setting up an SPF record involves adding a specific TXT record to your domain’s DNS settings.
You will need to obtain this record from your email service provider. The SPF record looks something like this:
After you obtain this from your email service provider, add this record to your domain’s DNS settings as a TXT record. Below is an example using Hostinger’s hpanel.
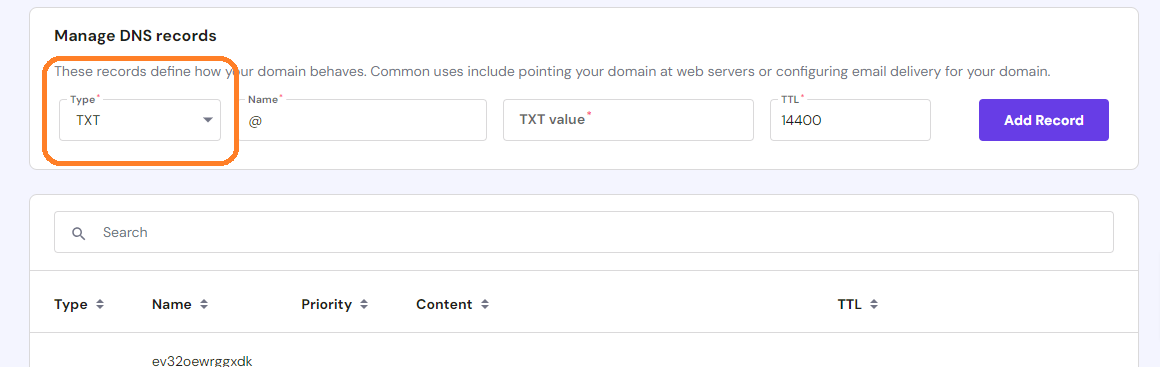
Step 3: Implement DKIM
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) records allow receiving servers to check that incoming mail from a domain is authorized by that domain’s administrators. Like the SPF records, this is given to you by your email service provider.
To implement DKIM you need to generate a pair of cryptographic keys (a private key and a public key). You should add the public key to your domain’s DNS records, and configure your email server to sign outgoing emails with the private key.
The DKIM record might look something like this:
These should be added to your domain’s DNS records as a CNAME record.

Step 4: Implement DMARC
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) records build on SPF and DKIM protocols, adding linkage to the sender’s domain. Implementing DMARC requires a good understanding of SPF and DKIM, so be sure to have those in place first.
However, you may not need to worry yourself about the technical details of how this works. The various email service providers make this easy for you by providing you with the DMARC policy record, which might look something like this:
All you need do is to add this record to your domain’s DNS settings as a TXT record.
As you may have noticed already DNS records can be complex, especially if you’re using multiple servers or third-party email services. So, be sure to double-check your records for accuracy. To check whether your email authentication protocols are in place, you can use the DMARC Record Lookup tool here.
IMPORTANT: While all of these may seem complex, implementing them is a crucial step in ensuring your emails are authenticated and delivered successfully. If you think you cannot do this by yourself, you can always reach out to your hosting service provider for help.
Monitoring and Optimizing for Success
After you’ve implemented SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, you must monitor your email performance and optimize as necessary. This is important because maintaining good email deliverability is an ongoing process. It requires regular monitoring, optimization, and a proactive approach to changes in email authentication requirements.
Here are a few tips that will ensure your emails continue to reach their intended recipients:
1. Using Postmaster Tools
Google Postmaster Tools and Yahoo Postmaster Tools provide valuable insights into your email performance. They allow you to track your domain reputation, spam complaint rates, and other important metrics. Here’s how to use them:
- Sign up for Google Postmaster Tools and Yahoo Postmaster Tools using your domain.
- Verify your domain ownership.
- Regularly check your dashboards for insights and alerts.
2. Identifying and Resolving Authentication Issues
Even with SPF, DKIM, and DMARC in place, you may encounter authentication issues. These could be due to changes in your email infrastructure, errors in your DNS records, or other factors. Here’s how to identify and resolve these issues:
- Use the data from your postmaster tools to identify any sudden changes in your metrics.
- If you notice an increase in authentication failures, check your DNS records for errors.
- If necessary, consult with your email service provider or a deliverability expert.
3. Maintain a Healthy Email List
Maintaining a clean and engaged email list is key to improving deliverability and engagement rates. Regularly remove inactive subscribers and those who have not engaged with your emails for a long time. Also, consider implementing a double opt-in process to ensure that your subscribers genuinely want to receive your emails.
4. Craft Engaging Content
Increasing your open rates and click-through rates is a surefire way to improve your email performance. Some techniques include crafting compelling subject lines, optimizing your email content for mobile devices, and sending your emails at the right time. This can improve your open rates and click-through rates, reducing the chances of your emails being marked as spam.
5. Use Personalization
Personalization can significantly improve your email engagement rates. By segmenting your email list and using dynamic content, you can tailor your emails to the specific needs and interests of each subscriber. This can lead to higher open rates, click-through rates, and overall engagement.
6. Unsubscribe Process
Ensuring a seamless and compliant unsubscribe process is not only a legal requirement but also a best practice for maintaining a healthy email list. Make sure your unsubscribe link is clearly visible in your emails, and honor unsubscribe requests promptly to maintain trust with your subscribers.
Remember, success in email marketing is not just about compliance. It’s about continuously optimizing your strategies and practices to deliver the best possible experience to your subscribers. And with these tips, you’re well on your way to achieving more success with email marketing.
Advanced Techniques for Ensuring Compliance
Apart from the above, there are a few techniques that can help you further optimize your email deliverability and performance. These include:
1. Warm-up Strategies
If you’re starting or have a new IP address, it’s important to increase your sending volume gradually. This process, known as “warming up,” helps to establish a positive sending reputation with email providers.
Start by sending low volumes of emails and then gradually increase your volume over time. This can help to avoid triggering spam filters and ensure your emails reach the inbox.
2. Blacklist Removal
Despite your best efforts, you may find your IP or domain on an email blacklist. This can happen if you’ve had a spike in spam complaints or if you’ve been identified as a source of spam. If this happens, don’t panic. Most blacklists provide information on why you were listed and how to request removal. Follow their instructions carefully and take steps to address the issue that led to the listing.
3. Domain Reputation Management
Your domain reputation plays a crucial role in your email deliverability. Email providers consider your domain’s reputation when deciding whether to deliver your emails to the inbox or the spam folder.
You can manage your domain reputation by following best practices for email deliverability, regularly monitoring your email performance, and promptly addressing any issues that arise.
Remember, success in email marketing requires a proactive approach and a commitment to continuous learning and optimization. By staying informed and adapting to changes, you can ensure your emails continue to reach their intended recipients and drive results for your business.
Recommended: Dominate Local Search with Google Business Profile Optimization (The Rank Math Advantage)
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the new email sender requirements set by Google and Yahoo?
The new Google and Yahoos new sender requirements are designed to combat spam and improve email security. These requirements primarily target large bulk senders, particularly those who send more than 5,000 emails a day. The key points include email authentication using DKIM, SPF, and DMARC, maintaining a spam complaint rate under 0.3%, ensuring a smooth unsubscribe process, compliance with RFC 5322, PTR records, and rDNS, and using a TLS connection for transmitting email.
Who will be impacted by the new requirements?
The new requirements will primarily impact large bulk senders, particularly those who send more than 5,000 emails a day. However, all email senders should be aware of these changes as they represent best practices in email deliverability and security.
What is the significance of the new requirements for email senders?
The new requirements aim to make email communication more secure and reliable. By implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, email senders can authenticate their emails, making it harder for spammers and phishers to impersonate their domains. This can lead to improved email deliverability and enhanced trust and engagement with recipients.
How to set up and maintain authentication for the sender’s domain?
Setting up and maintaining authentication for your domain involves adding SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records to your domain’s DNS settings. This process can be complex and requires a good understanding of DNS records. After implementing these measures, it’s important to monitor your email performance and make necessary adjustments. This could involve using postmaster tools to track compliance and performance, identifying and resolving authentication issues, and implementing advanced DMARC policies for stricter control and spam prevention.
What is the impact of non-compliance on email deliverability?
Non-compliance with the new email sender requirements can lead to your emails being marked as spam or even blocked entirely. This is because email providers like Google and Yahoo use SPF, DKIM, and DMARC as part of their spam filtering algorithms. If your emails fail these checks, they may be sent to the spam folder or blocked entirely. Additionally, non-compliance can damage your sender reputation, making it harder for your emails to reach their intended recipients.
What is the difference between Google and Yahoo’s requirements?
While both Google and Yahoo have announced new email sender requirements, the specifics may vary slightly between the two providers. However, both sets of requirements emphasize the importance of email authentication using SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, maintaining a low spam complaint rate, and using a TLS connection for email transmission. It’s important to stay up-to-date with announcements from both providers to ensure you’re complying with all requirements.
What is the role of email service providers in complying with the new requirements?
Email service providers play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with new requirements. They are responsible for implementing necessary changes in their systems, educating their users about the new requirements, and providing tools and resources to help users comply.
What is the importance of monitoring spam complaint rates?
Monitoring spam complaint rates is important as it helps senders identify potential issues with their email campaigns. High complaint rates can indicate that recipients are not finding the emails relevant or useful, which can harm the sender’s reputation and deliverability.
Conclusion
There you have it, your comprehensive guide to the new email sender requirements from Google and Yahoo. There’s no doubt that these requirements will significantly impact on the email marketing landscape.
In this post, we’ve emphasized the importance of understanding the new requirements and taking actionable steps for implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC authentication to ensure email deliverability. We’ve also delved into some advanced techniques and niche insights for optimizing your email performance.
The key takeaway is that implementing these new requirements is not just about compliance. It’s about proactively optimizing your email practices to ensure your emails continue to reach their intended recipients.
I encourage you, therefore, to implement these new requirements right away, even if you have not sent close to 5,000 bulk emails already. Start by verifying your domain, implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, and optimizing your email practices.
If you need some further help with this, feel free to check out Google’s official help page here. I’m sure you will be able to find some valuable insights to help you navigate any challenges you may encounter.
Remember, success in email marketing requires continuous learning and adaptation. So, let’s embrace these new requirements as an opportunity to improve our email practices and achieve better results.
Your turn: Have you implemented these new sender rules? What do you think of these new requirements? Share your thoughts with us in the comments below.





